Tech
What is chatgpt ? Everything you need to know

- What is ChatGPT?
- Who created ChatGPT?
- How does ChatGPT work?
- What kinds of questions can users ask ChatGPT?
- How are people using ChatGPT?
- What are the benefits of ChatGPT?
- What are the limitations of ChatGPT? How accurate is it?
- What are the ethical concerns associated with ChatGPT?
- What are the ethical concerns associated with ChatGPT?
- How can you access ChatGPT?
- Is ChatGPT free?
- What are the alternatives to ChatGPT?
- ChatGPT updates 2023
- Chat GPT Update 2024
What is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is an artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot that uses natural language processing to create humanlike conversational dialogue. The language model can respond to questions and compose various written content, including articles, social media posts, essays, code and emails.
ChatGPT is a form of generative AI — a tool that lets users enter prompts to receive humanlike images, text or videos that are created by AI.
ChatGPT is similar to the automated chat services found on customer service websites, as people can ask it questions or request clarification to ChatGPT’s replies. The GPT stands for “Generative Pre-trained Transformer,” which refers to how ChatGPT processes requests and formulates responses. ChatGPT is trained with reinforcement learning through human feedback and reward models that rank the best responses. This feedback helps augment ChatGPT with machine learning to improve future responses.
Who created ChatGPT?
OpenAI — an artificial intelligence research company — created ChatGPT and launched the tool in November 2022. It was founded by a group of entrepreneurs and researchers including Elon Musk and Sam Altman in 2015. OpenAI is backed by several investors, with Microsoft being the most notable. OpenAI also created Dall-E, an AI text-to-art generator.
How does ChatGPT work?
ChatGPT works through its Generative Pre-trained Transformer, which uses specialized algorithms to find patterns within data sequences. ChatGPT originally used the GPT-3 large language model, a neural network machine learning model and the third generation of Generative Pre-trained Transformer. The transformer pulls from a significant amount of data to formulate a response.
ChatGPT now uses the GPT-3.5 model that includes a fine-tuning process for its algorithm. ChatGPT Plus uses GPT-4, which offers a faster response time and internet plugins. GPT-4 can also handle more complex tasks compared with previous models, such as describing photos, generating captions for images and creating more detailed responses up to 25,000 words.
ChatGPT uses deep learning, a subset of machine learning, to produce humanlike text through transformer neural networks. The transformer predicts text — including the next word, sentence or paragraph — based on its training data’s typical sequence.
Training begins with generic data, then moves to more tailored data for a specific task. ChatGPT was trained with online text to learn the human language, and then it used transcripts to learn the basics of conversations.
Human trainers provide conversations and rank the responses. These reward models help determine the best answers. To keep training the chatbot, users can upvote or downvote its response by clicking on thumbs-up or thumbs-down icons beside the answer. Users can also provide additional written feedback to improve and fine-tune future dialogue.
What kinds of questions can users ask ChatGPT?
Users can ask ChatGPT a variety of questions, including simple or more complex questions, such as, “What is the meaning of life?” or “What year did New York become a state?” ChatGPT is proficient with STEM disciplines and can debug or write code. There is no limitation to the types of questions to ask ChatGPT. However, ChatGPT uses data up to the year 2021, so it has no knowledge of events and data past that year. And since it is a conversational chatbot, users can ask for more information or ask it to try again when generating text.
How are people using ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is versatile and can be used for more than human conversations. People have used ChatGPT to do the following:
- Code computer programs and check for bugs in code.
- Compose music.
- Draft emails.
- Summarize articles, podcasts or presentations.
- Script social media posts.
- Create titles for articles.
- Solve math problems.
- Discover keywords for search engine optimization.
- Create articles, blog posts and quizzes for websites.
- Reword existing content for a different medium, such as a presentation transcript for a blog post.
- Formulate product descriptions.
- Play games.
- Assist with job searches, including writing resumes and cover letters.
- Ask trivia questions.
- Describe complex topics more simply.
- Write video scripts.
- Research markets for products.
- Generate art.
Unlike other chatbots, ChatGPT can remember various questions to continue the conversation in a more fluid manner.

What are the benefits of ChatGPT?
Businesses and users are still exploring the benefits of ChatGPT as the program continues to evolve. Some benefits include the following:
- Efficiency. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine and repetitive tasks, which can free up employees to focus on more complex and strategic responsibilities.
- Cost savings. Using AI chatbots can be more cost-effective than hiring and training additional employees.
- Improved content quality. Writers can use ChatGPT to improve grammatical or contextual errors or to help brainstorm ideas for content. Employees can take ordinary text and ask to improve its language or add expressions.
- Education and training. ChatGPT can help provide explanations on more complex topics to help serve as a virtual tutor. Users can also ask for guides and any needed clarification on responses.
- Better response time. ChatGPT provides instant responses, which reduces wait times for users seeking assistance.
- Increased availability. AI models are available around the clock to provide continuous support and assistance.
- Multilingual support. ChatGPT can communicate in multiple languages or provide translations for businesses with global audiences.
- Personalization. AI chatbots can tailor responses to the user’s preferences and behaviors based on previous interactions.
- Scalability. ChatGPT can handle many users simultaneously, which is beneficial for applications with high user engagement.
- Natural language understanding. ChatGPT understands and generates humanlike text, so it is useful for tasks such as generating content, answering questions, engaging in conversations and providing explanations.
- Digital accessibility. ChatGPT and other AI chatbots can assist individuals with disabilities by providing text-based interactions, which can be easier to navigate than other interfaces.
What are the limitations of ChatGPT? How accurate is it?
Some limitations of ChatGPT include the following:
- It does not fully understand the complexity of human language. ChatGPT is trained to generate words based on input. Because of this, responses might seem shallow and lack true insight.
- Lack of knowledge for data and events after 2021. The training data ends with 2021 content. ChatGPT can provide incorrect information based on the data from which it pulls. If ChatGPT does not fully understand the query, it might also provide an inaccurate response. ChatGPT is still being trained, so feedback is recommended when an answer is incorrect.
- Responses can sound like a machine and unnatural. Since ChatGPT predicts the next word, it can overuse words such as the or and. Because of this, people still need to review and edit content to make it flow more naturally, like human writing.
- It summarizes but does not cite sources. ChatGPT does not provide analysis or insight into any data or statistics. ChatGPT might provide statistics but no real commentary on what these statistics mean or how they relate to the topic.
- It cannot understand sarcasm and irony. ChatGPT is based on a data set of text.
- It might focus on the wrong part of a question and not be able to shift. For example, if you ask ChatGPT, “Does a horse make a good pet based on its size?” and then ask it, “What about a cat?” ChatGPT might focus solely on the size of the animal versus giving information about having the animal as a pet. ChatGPT is not divergent and cannot shift its answer to cover multiple questions in a single response.
What are the ethical concerns associated with ChatGPT?
What are the ethical concerns associated with ChatGPT?
While ChatGPT can be helpful for some tasks, there are some ethical concerns that depend on how it is used, including bias, lack of privacy and security, and cheating in education and work.
Plagiarism and deceitful use
ChatGPT can be used unethically in ways such as cheating, impersonation or spreading misinformation due to its humanlike capabilities. Educators have brought up concerns about students using ChatGPT to cheat, plagiarize and write papers. CNET made the news when it used ChatGPT to create articles that were filled with errors.
To help prevent cheating and plagiarizing, OpenAI announced an AI text classifier to distinguish between human- and AI-generated text. However, after six months of availability, OpenAI pulled the tool due to a “low rate of accuracy.”
There are online tools, such as Copyleaks or Writing.com, to classify how likely it is that text was written by a person versus being AI-generated. OpenAI plans to add a watermark to longer text pieces to help identify AI-generated content.
Because ChatGPT can write code, it also presents a problem for cybersecurity. Threat actors can use ChatGPT to help create malware. An update addressed the issue of creating malware by stopping the request, but threat actors might find ways around OpenAI’s safety protocol.
ChatGPT can also be used to impersonate a person by training it to copy someone’s writing and language style. The chatbot could then impersonate a trusted person to collect sensitive information or spread disinformation.
Bias in training data
One of the biggest ethical concerns with ChatGPT is its bias in training data. If the data the model pulls from has any bias, it is reflected in the model’s output. ChatGPT also does not understand language that might be offensive or discriminatory. The data needs to be reviewed to avoid perpetuating bias, but including diverse and representative material can help control bias for accurate results.
Replacing jobs and human interaction
As technology advances, ChatGPT might automate certain tasks that are typically completed by humans, such as data entry and processing, customer service, and translation support. People are worried that it could replace their jobs, so it’s important to consider ChatGPT and AI’s effect on workers.
Rather than replacing workers, ChatGPT can be used as support for job functions and creating new job opportunities to avoid loss of employment. For example, lawyers can use ChatGPT to create summaries of case notes and draft contracts or agreements. And copywriters can use ChatGPT for article outlines and headline ideas.
Privacy issues
ChatGPT uses text based on input, so it could potentially reveal sensitive information. The model’s output can also track and profile individuals by collecting information from a prompt and associating this information with the user’s phone number and email. The information is then stored indefinitely.
How can you access ChatGPT?
To access ChatGPT, create an OpenAI account. Go to chat.openai.com and then select “Sign Up” and enter an email address, or use a Google or Microsoft account to log in.
After signing up, type a prompt or question in the message box on the ChatGPT homepage. Users can then do the following:
- Enter a different prompt for a new query or ask for clarification.
- Regenerate the response.
- Share the response.
- Like or dislike the response with the thumbs-up or thumbs-down option.
- Copy the response.
What to do if ChatGPT is at capacity?
Even though ChatGPT can handle numerous users at a time, it reaches maximum capacity occasionally when there is an overload. This usually happens during peak hours, such as early in the morning or in the evening, depending on the time zone.
If it is at capacity, try using it at different times or hit refresh on the browser. Another option is to upgrade to ChatGPT Plus, which is a subscription, but is typically always available, even during high-demand periods.
Is ChatGPT free?
ChatGPT is available for free through OpenAI’s website. Users need to register for a free OpenAI account. There is also an option to upgrade to ChatGPT Plus for access to GPT-4, faster responses, no blackout windows and unlimited availability. ChatGPT Plus also gives priority access to new features for a subscription rate of $20 per month.
Without a subscription, there are limitations. The most notable limitation of the free version is access to ChatGPT when the program is at capacity. The Plus membership gives unlimited access to avoid capacity blackouts.
What are the alternatives to ChatGPT?
Because of ChatGPT’s popularity, it is often unavailable due to capacity issues. Google announced Bard in response to ChatGPT. Google Bard will draw information directly from the internet through a Google search to provide the latest information.
Microsoft added ChatGPT functionality to Bing, giving the internet search engine a chat mode for users. The ChatGPT functionality in Bing isn’t as limited because its training is up to date and doesn’t end with 2021 data and events.
There are other text generator alternatives to ChatGPT, including the following:
- AI-Writer.
- Article Forge.
- ChatSonic.
- Copysmith.
- DeepL Write.
- Google Bard.
- Jasper.
- Magic Write.
- Open Assistant.
- Peppertype.
- Perplexity AI.
- Spellbook.
- Rytr.
- YouChat.
Coding alternatives for ChatGPT include the following:
- AlphaCode.
- Amazon CodeWhisperer.
- CodeStarter.
- CodeWP.
- Cody.
- Enzyme.
- Ghostwriter.
- GitHub Copilot.
- Mutable.ai.
- OpenAI Codex.
- Seek.
- Tabnine.
ChatGPT updates 2023
In August 2023, OpenAI announced an enterprise version of ChatGPT. The enterprise version offers the higher-speed GPT-4 model with a longer context window, customization options and data analysis. This model of ChatGPT does not share data outside the organization.
In September 2023, OpenAI announced a new update that allows ChatGPT to speak and recognize images. Users can upload pictures of what they have in their refrigerator and ChatGPT will provide ideas for dinner. Users can engage to get step-by-step recipes with ingredients they already have. People can also use ChatGPT to ask questions about photos — such as landmarks — and engage in conversation to learn facts and history.
Users can also use voice to engage with ChatGPT and speak to it like other voice assistants. People can have conversations to request stories, ask trivia questions or request jokes among other options.
The voice update will be available on apps for both iOS and Android. Users will just need to opt-in to use it in their settings. Images will be available on all platforms — including apps and ChatGPT’s website.
In November 2023, OpenAI announced the rollout of GPTs, which let users customize their own version of ChatGPT for a specific use case. For example, a user could create a GPT that only scripts social media posts, checks for bugs in code, or formulates product descriptions. The user can input instructions and knowledge files in the GPT builder to give the custom GPT context. OpenAI also announced the GPT store, which will let users share and monetize their custom bots.
In December 2023, OpenAI partnered with Axel Springer to train its AI models on news reporting. ChatGPT users will see summaries of news stories from Bild and Welt, Business Insider and Politico as part of this deal. This agreement gives ChatGPT more current information in its chatbot answers and gives users another way to access news stories. OpenAI also announced an agreement with the Associated Press to use the news reporting archive for chatbot responses.
Chat GPT Update 2024
Introducing the GPT Store and ChatGPT Team plan (Jan 10, 2024)
Discover what’s trending in the GPT Store
The store features a diverse range of GPTs developed by our partners and the community. Browse popular and trending GPTs on the community leaderboard, with categories like DALL·E, writing, research, programming, education, and lifestyle.
Explore GPTs at chat.openai.com/gpts.
Use ChatGPT alongside your team
ChatGpt launching a new ChatGPT plan in 2024 for teams of all sizes, which provides a secure, collaborative workspace to get the most out of ChatGPT at work.
ChatGPT Team offers access to our advanced models like GPT-4 and DALL·E 3, and tools like Advanced Data Analysis. It additionally includes a dedicated collaborative workspace for your team and admin tools for team management. As with ChatGPT Enterprise, you own and control your business data — we do not train on your business data or conversations, and our models don’t learn from your usage. More details on our data privacy practices can be found on our privacy page and Trust Portal.
News
Ex-Secret Service special agents explain why counter-sniper who saved Trump’s life may have lost crucial seconds
Story by litaliano@insider.com (Laura Italiano)
- Trump’s life was saved by a Secret Service counter-sniper assigned to Saturday’s detail.
- But the shooter still managed to kill one rally-goer and injure two others before he was taken out.
- Experts said heat, staffing, and a focus on a nearby treeline may have cost crucial seconds.
The Secret Service counter-sniper who narrowly saved the life of former President Donald Trump may have lost crucial seconds due to a number of factors, including the extreme heat, a lack of anti-sniper backup, and a likely focus on a nearby treeline, a former special agent told Business Insider.
“This counter-sniper made an amazingly quick decision and clearly saved Trump’s life,” said Bill Pickle, the former special agent in charge of Al Gore’s vice-presidential Secret Service detail.
“Our guys are the best shots in the world. That’s what they do,” Pickle said.
“And within a second of the moment this kid opened fire, the CS guy shot him,” he said, using Secret Service shorthand for the counter-sniper deployed at Saturday night’s rally in Butler, Pennsylvania.
“But someone will blame that CS and the spotter, and say, ‘If only he had been two seconds faster in spotting the shooter,'” the former special agent said.
“The real question may be, if there were more anti-sniper eyes on that building, could this have all been avoided.”
How did the counter-sniper team not see the shooting suspect sooner?
Pickle said one area of focus for investigators will be how the shooter managed to get on top of the building without authorities taking notice.
“The other question is, why wasn’t this roof secured, and were there agents or law enforcement in there checking IDs?” he added.
“How did this kid figure out a way to get out on the rooftop and slither across that rooftop?” Pickle said. “He low-crawled across the roof on his hands and knees, and he pushed the weapon ahead of him just like in the military.”
But even if they had seen the shooting suspect more quickly, counter-snipers may not always have the ability to act immediately when they spot a threat, according to Anthony Cangelosi, a former special agent who directed the Secret Service’s technical security advances for presidential candidates.
“You either have to make a decision: ‘Do I take a shot? Or do I not take a shot?'” Cangelosi told Business Insider.
“What if you find out, ‘Oh, I just killed a 20-year-old kid who loves the protectee, and he couldn’t get in the venue, and he just wanted to get up on that roof?’ No one wants to be in that position,” Cangelosi said.
Cangelosi said the Secret Service team at the event should have a “site plan” that would include a layout of the area and the surrounding buildings.
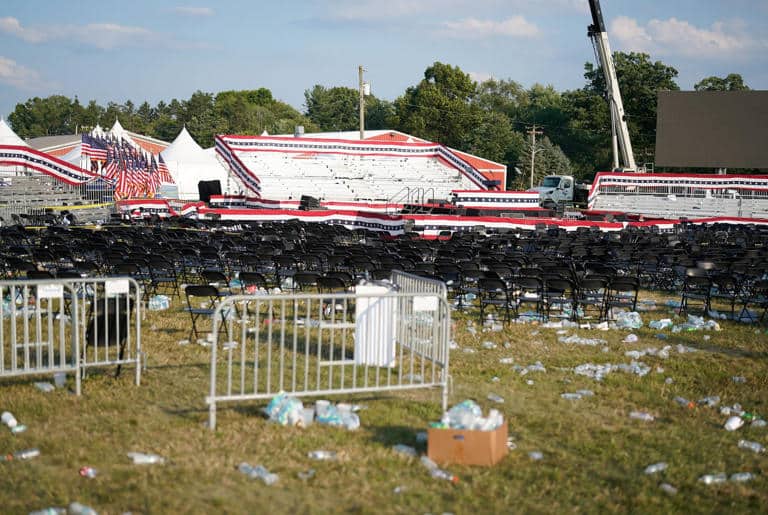

The would-be assassin fired at least three rounds from a rooftop 150 yards from where Trump was speaking. He killed one rally-goer and critically injured two others before being shot dead by a yet-identified Secret Service counter-sniper, who was positioned on another rooftop.
One bullet grazed Trump’s right ear, bloodying his face.
“This kid, at 150 yards, made a great shot,” Pickle said Sunday of the would-be assassin, his voice grim. “I don’t know the specifics of whether he used optics, meaning a scope on his rifle,” he told BI.
“But even with optics, it takes somebody with training to aim at somebody’s head from 150 yards away, and you actually hit the edge of the head,” he said.
“That’s not a lucky shot. That’s a guy who actually shot before.”
The FBI identified the shooter as 20-year-old Thomas Matthew Crooks of Bethel Park, Pennsylvania. The FBI said they are still investigating a motive.
But for now, it’s clear that at least three things may have factored into the several-second delay between when Crooks was seen crawling onto the roof and when the CS team saw and shot him, Pickle said.
The decision on how many anti-snipers to deploy may prove the most critical factor, he said.
“Someone made a decision that that number of counter-snipers was sufficient,” he said. “And obviously, in hindsight, they were wrong because there was a kid who was able to get up there on that rooftop and pull the trigger three times at least.”
How many CS teams were deployed?

Staffing decisions would have been made at Secret Service headquarters in Washington, based on whatever agency personnel on the ground recommended after a several-day investigation of the site, Pickle said.
“An advance team actually does a lengthy survey, where they look at everything and then recommend what they need,” he said.
“But if they’re stretched for resources, headquarters can say we can only get you one team out there. And that’s not unusual — if you don’t have it, you don’t have it,” Pickle said.
“It always boils down to resources,” he said. “And if it’s not a resource problem, and the money was there, then it’s still an allocation of resources problem,” he said — meaning someone underestimated the manpower needed to keep Trump safe.
Regardless of how many snipers were present, the Secret Service would typically have “360-degree coverage” of an event where a sitting or former president is speaking, Cangelosi said.
Other factors include the weather.
“The CS guys would probably say we were up there for four hours in 100-degree heat, and if we had another team up here or drone support this wouldn’t have happened,” Pickle said.
The team may also have been focusing on a nearby tree line, seeing it as the primary risk.
“You’re looking at everything that would hide a potential assassin,” Pickle said.
“The first assumption is that if I’m a bad guy, I’m going to hide. Human nature is such that I’m going to be scanning the rooftops, to make sure they’re empty, but then I’m going to be focusing on that tree line because you think the bad guy is going to be hidden,” Pickle said.
“You don’t think the bad guy is going to be out in the open,” he said..
Inter-agency squabbles and intense public scrutiny are forthcoming
Once the would-be assassin opened fire, “everything that happened up there was textbook and the way it should have happened,” Pickle said. The CS team returned fire, long-gun-toting counter-assault agents in black jumpsuits and helmets rushed the stage, and business-suited agents on the rally platform hurried Trump off stage.
“But why wasn’t he identified seconds sooner?” Pickle asked of the shooter.
“Was it caused by exhaustion from being on a 100-degree roof for four hours? Was the CS team watching the heavy foliage there, which arguably was the best place to hide?” he asked.
“An open roof is not the best place to hide. If he climbed out onto an open rooftop, he was prepared to die,” he added.
“The worst nightmare for the Secret Service has always been a lone gunman who hasn’t been announcing his views publicly and is ready to die.”
Pickle said Saturday’s incident will be dissected for years to come and “will be in the training syllabus forever.”
“It’s going to be a circular firing squad,” Pickle predicted of the inter-agency finger-pointing and conspiracy theories that will play out as the attempted assassination is scrutinized by the FBI, Congress, and the press and public.
“This thing will be dissected for years, and it will be in the training syllabus forever,” he said.
Cangelosi told BI that “a lot of people talk and things just travel” within the agency after an event of this magnitude.
“We all want answers, and we want them as quickly as possible, but it’s it’s going to take some time,” Cangelosi said. “You know the Secret Service; they’re professionals. Mistakes are made, they’re going to remedy them.”
If you enjoyed this story, be sure to follow TheFactsPk on Facebook Page.
News
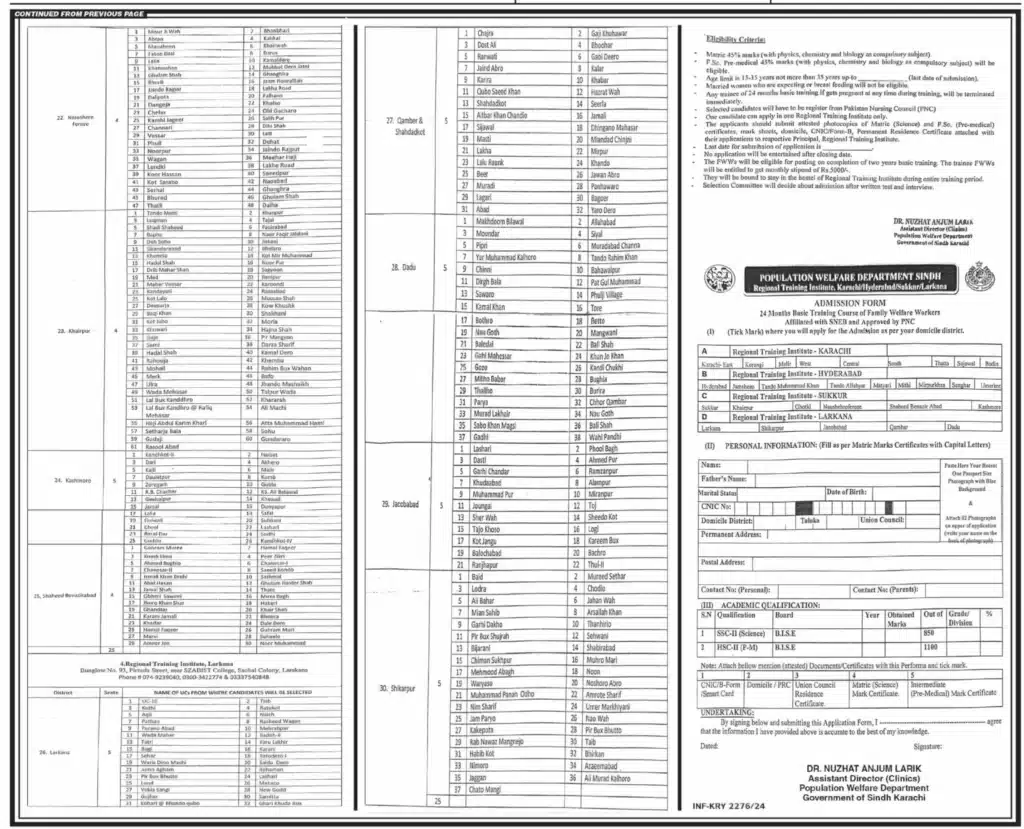
Family Welfare Workers Jobs 2024

Candidates looking for Related searches for Family Welfare Workers Jobs 2024, Family Welfare Workers Training Programs 2024, FWW Jobs 2024, PWD Sindh Job Vacancies 2024, Sindh Population Welfare Department Careers, Apply for PWD Sindh Jobs, PWD Sindh Recruitment 2024, Government Jobs in Sindh 2024, Population Welfare Department Hiring 2024, Sindh PWD Job Application, have to read this crucial topic and apply for the open positions listed below. To fill positions: Family Welfare Workers
Eligibility Criteria for Family Welfare Workers Jobs 2024
Other Skills:
- Proficiency in medical terminology and patient care protocols.
- Strong communication and interpersonal skills.
- Ability to work effectively in a team-oriented environment.
Institutes to Apply:
- Regional Training Institute, Karachi
- Regional Training Institute, Hyderabad
- Regional Training Institute, Sukkur
- Regional Training Institute, Larkana
Stipend and Accommodation:
- Trainees will receive a monthly stipend of Rs. 5000.
- Trainees must stay in the hostel of the Regional Training Institute during the entire training period.
Conditions:
- Matric 45% marks (with physics, chemistry, and biology as compulsory subjects).
- F.Sc. Pre-medical 45% marks (with physics, chemistry, and biology as compulsory subjects) will be eligible.
- The age limit is 15-35 years not more than 35 years up to,
- Married women who are expecting or breastfeeding will not be eligible.
- (last date of submission).
- Any trance of 24 months of basic training if one gets pregnant at any time during training, will be terminated immediately.
- Selected candidates will have to register with the Pakistan Nursing Council (PNC)
- One candidate can apply to one Regional Training Institute only.
Vacant Positions
Family Welfare Workers Jobs 2024 Apply:
- 1- Document Submission: Send a detailed CV, attested copies of educational and experience certificates, 01 recent photo, Matric (Science) certificate and mark sheet, F.Sc. (Pre-medical) certificate and mark sheet, and a copy of CNIC.
- 2- Submission address: Dr. Nuzhat Anjum Larik Assistant Director (Clinics) Population Welfare Department Government of Sindh, Karachi
- 3- Government/public sector company employees should apply through proper channels.
- 4- All job seekers are requested to visit the PWD website for more information.
Important FAQs About Population Welfare Department Hiring 2024:
What are the eligibility requirements?
Applicants must have a Matric, and Intermediate qualification and relevant field experience.
Where are the job locations?
Karachi
When is the deadline to apply?
July 29, 2024
How to Apply?
To apply for the 24 Months Basic Training Course of Family Welfare Workers in Sindh, candidates must meet educational requirements (Matric or F.Sc. Pre-medical), age criteria (15-35 years), and submit required documents to their chosen Regional Training Institute (Karachi, Hyderabad, Sukkur, Larkana). The selection process includes a written test and interview, with selected trainees receiving a monthly stipend and accommodation during training.
Population Welfare Department Sindh Jobs 2024 Advertisement:
News
What is Devin? The AI software engineer everyone is talking about

Discover the groundbreaking AI software engineer, Devin, designed to revolutionize software development through collaboration with humans. Explore Devin’s capabilities, origins, impact, and future outlook.
Devin is not just a program; it’s a groundbreaking AI that acts as a software engineer, capable of coding, debugging, and even developing apps and websites. Created by Cognition and led by Scott Wu, Devin represents a significant leap in AI’s role in software development. It’s designed to work alongside humans, enhancing productivity rather than replacing jobs. With abilities to learn and adapt, Devin is reshaping how software engineering tasks are approached, promising a future where AI and humans collaborate more closely. Here’s a quick look at what Devin brings to the table:
- AI as a Software Engineer: Devin can handle coding, testing, and deployment autonomously in multiple programming languages.
- Learning and Adapting: It learns from each project, improving its efficiency and capabilities over time.
- Collaboration with Humans: Designed to assist rather than replace human engineers, enhancing team productivity.
- Real-World Applications: From website creation to app development and software testing, Devin has already shown its potential in actual projects.
This intro not only highlights Devin’s capabilities but also emphasizes its role in the future of software engineering, focusing on collaboration between AI and humans for enhanced productivity and innovation.
Origins and Creator
Cognition, the company behind Devin, is led by a guy named Scott Wu. They focus on making AI smarter, especially in solving problems. With Devin, their aim is to have an AI “buddy” that can team up with real engineers. Devin can handle the day-to-day stuff, which lets engineers solve bigger, tougher problems.
Brief History of AI in Software Engineering
AI has been around in coding for a long time but in small ways:
- Tools in coding programs (IDEs) use AI to guess what you’re going to type next.
- Some programs automatically check your code for mistakes or style issues.
- There are AI tools that can chat with you while you code, giving advice.
Devin is a big step up from these. It’s the first AI that can fully take on coding tasks by itself, from start to finish. Before Devin, AI tools were more like helpers, focusing on one thing at a time. Devin can understand big tasks and handle them on its own.
Capabilities of Devin
Devin is like a super-smart robot that knows how to code. It’s made to help with building and improving software, which is a big deal for people who make apps and websites.
Coding, Testing, and Deployment
- Coding: Devin can write in many computer languages like Python and JavaScript. It can make all sorts of things, like websites, apps, and more, just by understanding what you need.
- Testing: It checks its own work for mistakes to make sure everything runs smoothly and does what it’s supposed to do.
- Deployment: After making something, Devin can set it up on the internet or wherever it needs to go, making sure it works well for everyone.
- Adapting and learning: Devin gets better over time. It learns new tech stuff, picks up new skills, and uses them to tackle new challenges.
Advanced Features
- Planning and reasoning: Devin can figure out how to build complex software, breaking big projects into smaller tasks before starting to code. It thinks through problems to find the best solutions.
- Recalling context: It remembers important details about the project, like what the goal is and what tools to use, so it doesn’t get mixed up.
- Self-correction: As Devin works more, it learns how to do things better and can update how it works all by itself.
- Training AI models: Devin can also train mini-robot brains to do specific tasks within a project, like making predictions or recommendations.
With Devin, the goal is to make the job of software engineers easier by doing a lot of the heavy lifting, while still working well with humans.
How Devin Works
Devin is pretty smart. It uses some of the latest AI tech to figure out what you need, plan how to do it, write code, and even fix its own mistakes.
Algorithms and Knowledge Base
Think of Devin as having a huge library in its head. It knows a lot about different programming languages, how to build software, and the best ways to get things done. When you ask Devin to do something, it uses this library to understand your request.
First, Devin breaks down what you’ve asked into smaller pieces it can understand. Then, it digs into its library to find the best way to tackle your request. It thinks about things like how fast it needs to work, how big the project is, and how to make everything run smoothly.
After planning, Devin starts writing code. It knows languages like Python and JavaScript and can figure out the best way to put everything together. Devin also checks its work to make sure it all makes sense.
As Devin works on more projects, it learns and gets even better. This means it can handle new challenges and keep up with the latest tech stuff.
Integration with Teams
Devin isn’t just working alone; it’s part of the team. It can talk to human engineers, update them on what it’s doing, and get their feedback.
Devin does the routine stuff like writing basic code and checking for mistakes. This lets the human engineers focus on the trickier problems. Working together, they can build things faster and more creatively.
Devin also learns from working with the team. It gets better by understanding the team’s style and preferences. This learning makes Devin a better team player over time.
In short, Devin is like a super-helpful robot that knows a lot about coding. It works with human engineers, doing the heavy lifting so they can focus on solving big problems. Together, they make a great team, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in tech.
Real-World Impact
Devin is designed to work with engineers to help them do their jobs better, not to take their jobs away. So far, it’s been pretty good at solving software problems and helping with actual projects.
Performance Metrics
In tests, Devin managed to solve about 14 out of every 100 software problems it was given. That’s a big deal because older AI models could only solve about 2 out of 100. These tests show that Devin is really good at:
- Finding and fixing errors in code
- Pointing out mistakes in how the code is set up
- Offering ways to make the code better
And as Devin learns more, it’s expected to get even better at these things.
Use Cases
Devin has been put to work on real projects, like on freelance job sites such as Upwork. Here are some ways people have used Devin:
- Website Creation: Devin has made websites for clients, taking care of how the site looks and connecting it to databases. People were happy with the work.
- App Development: For a mobile app, Devin helped design the look of the app and write the code that makes the app work. This made the development process faster.
- Software Testing: Devin was used to check software for problems, find those issues, and suggest how to fix them. This let the human engineers focus more on creating new features.
These examples show that Devin can work well with human teams on real projects. By doing the routine tasks, it lets engineers aim for bigger goals.
Future Outlook
Possibilities
Devin is showing us what the future might look like for AI in coding. It’s like a sneak peek into a world where AI can do even more amazing things. Imagine Devin or similar AI tools in the future being able to:
- Handle really big and complicated coding projects all by themselves
- Look after huge amounts of code
- Take care of complex software systems
- Come up with new ways to solve problems, maybe even inventing new kinds of code
- Teach other AI to handle special coding tasks
- Make software that gets better on its own
Right now, Devin is still learning. It can’t fully grasp the deeper meaning of what it’s coding. But as AI gets smarter, it could start doing things we usually think only humans can do, like designing better software or coming up with new tech ideas.
Broader Influence
As AI like Devin gets better, it’s going to change how we think about coding jobs. But it’s not all about taking away jobs. Here’s how Devin and AI can actually help:
- They can do the boring code work, so humans can think up new ideas
- Make creating software faster and less of a hassle
- Help people who don’t know much about coding make their own programs
- Lead to new ways of coding with AI’s help
- Change how software teams work, making AI a key team member
- Increase the need for people who know how to work with AI in coding
AI helpers like Devin won’t replace coders. Instead, they’ll become important teammates, helping bring to life the next big things in tech. Learning to work with AI in coding is going to be a big deal for anyone in tech.
FAQs
– Will Devin replace programmers?
No, Devin is here to work with people, not take their jobs. It’s made to do the everyday coding stuff so that human programmers can tackle bigger challenges. Even as AI gets smarter, things like coming up with new ideas and working with others are still very much a human job.
– Who created Devin AI?
A company named Cognition made Devin. Scott Wu started this company, and it’s filled with smart people who know a lot about AI, making software, and turning ideas into products.
– Will coding be obsolete in the next 5 years?
Coding won’t disappear in the next 5 years. AI like Devin can take over some parts of coding, but humans are still needed for the creative and tough parts. The future will likely see people and AI working together more, using both their strengths.
– Who is the world’s first AI CEO?
In 2014, a company called Deep Knowledge Ventures made history by adding an AI system named VITAL to its board. VITAL wasn’t exactly a CEO but did have a big role in making decisions, which was a first.
– Who is the godfather of AI?
John McCarthy is often called the godfather of AI because he came up with the name “artificial intelligence” in 1955. He also helped start the whole field of AI with a big meeting in 1956 and worked on many key ideas in AI.
Conclusion
Devin is a big deal because it’s the first AI that can do the job of a software engineer all by itself. It’s really good at figuring out how to solve coding problems and can even teach other AI how to do specific tasks. This is a big step forward in how smart AI is becoming.
Here’s what makes Devin so important:
- Makes work faster: Devin can do a lot of the regular coding work, which means the human coders can spend more time on coming up with new ideas. This could make the whole team get more done.
- New ways to work together: Having an AI like Devin on the team means people can think of new ways to work with AI. It’s like having a super smart helper that’s always ready.
- Speeds up making software: Devin can do coding, testing, and putting software out there much quicker. This means we can see new apps and websites faster than before.
- Easier for everyone: Devin can make it easier for people who don’t know how to code to make their own software. It’s kind of like having a coding helper that does the hard work for you.
- Changing jobs: As AI like Devin gets better, we might need to think differently about what it means to be a software engineer. There might be more jobs for people who know how to work with AI developers.
Devin starting to work like a real software engineer is exciting because it could change how we make software. While some people are worried about jobs changing, Devin also offers a lot of good things, like making it easier to create new technology.
Related Questions
What is Devin AI software?
Devin is a smart tool that helps with coding by itself. It can understand what you want to make, write the code, find and fix errors, and get better over time by learning. Devin’s goal is to take care of the routine coding tasks so that human coders can focus on more complex problems.
How does Devin work?
Devin uses smart tech to understand your coding requests and turn them into actual code. It plans, writes, tests, and fixes code in different programming languages like Python and JavaScript. Devin also works with coding teams by doing the basic coding tasks, letting the human coders tackle the harder stuff.
What does an AI engineer do?
AI engineers create the brains behind AI applications. They write the programs that make AI work, run tests to learn and improve AI, create data AI can learn from, make sure AI is working well, and keep up with new discoveries in AI.
Are software engineers worried about AI?
Yes, some coders are concerned that AI might do a lot of their job in the future, which could mean fewer jobs for them. However, AI is also expected to create new types of jobs, like specialists in AI apps, data experts, and roles focused on making sure AI is used responsibly. Being open to learning new things will be important.